
Plant Allergy Overview
Allergenicity
Moderate
Pollen Season
Winter Spring
Type
Tree
Sub-Type
Deciduous
Allergy Information
Birch species are reported to cause severe pollinosis where large numbers are present, and cause the same types of allergies. Pollen allergenicity has been well documented in Europe. Birches have been reported to rank second to the oaks in importance for causing pollinosis among tree types. Birch pollen allergenicity has been reported to be more frequent east of the Rocky Mountains.
Genus Details
Several native European and Asian species are found in the U.S., usually in the northern states. Birch are graceful, columnar trees that grow 60 to 100 feet tall and have simple, alternate leaves. The resinous, scaly bark is composed of papery layers with prominent, horizontal, corky spots. Flowers occur as separate pendulous staminate catkins and smaller, upright pistillate (cone-like) catkins on the same tree. Flowering occurs in early spring before or at the time leaves appear for a short period of about 7 days. All species are wind-pollinated and species flower in succession at different times, some species overlapping, so massive amounts of pollen may shed over several weeks.
Pollen Description
The grains are suboblate to oblate; the amb triangular with convex sides. The pollen has 3 strongly-aspidate pores.
Grains are 18-23 x 21-30 micrometers in size.
Genus Distribution
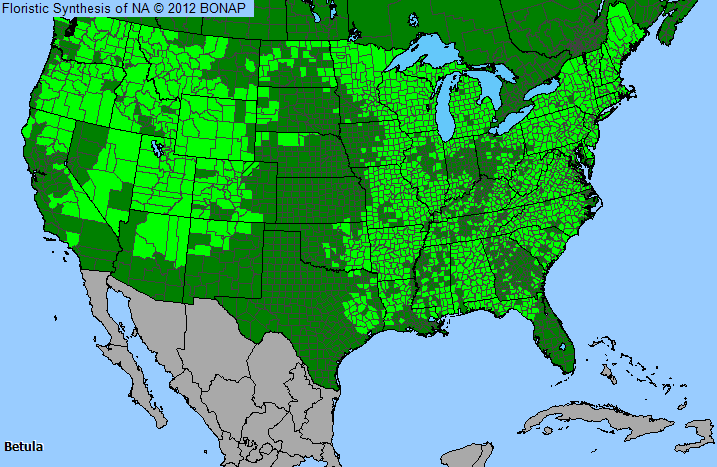
The shaded areas on the map indicates where the genus has been observed in the United States.
 - Native, observed in a county
- Native, observed in a county  - Introduced, observed in a county
- Introduced, observed in a county  - Rarely observed
- Rarely observedSpecies in Birch Genus
Allergens & Plants Search
Enter a full or partial species name to find more information on one of over 1,200 potentially allergenic plants.
For example, you can find chenopods searching on "cheno"


